Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene, or UHMW-PE. Not the most catchy moniker, but you can blame a chemist for that. This plastic more than makes up for the inconvenience with its super powers: Whether you need parts that are crazy durable, have great chemical resistance, or super low friction characteristics, you’ve chosen the right material.
What is UHMW?
Ultra High Molecular Weight (or UHMW for convenience) is a high performance variant of the thermoplastic polyethylene, and can be found in numerous applications from infrastructure to consumer goods.
UHMW was first offered commercially in the 1950s and over the years has been refined, combined with other materials such as aramid fibers or ceramic powder, hit with gamma radiation to change its microscopic structural properties, and even infused (cross-linked) with vitamin E to be used in medical applications.
Quite often, however, standard UHMW exhibits the best material properties over the widest range of conditions, including a working temperature range from -22°F to 180°F, impact and corrosion resistance better than most metal alloys, FDA food-grade designation, and virtual immunity to water absorption.
In industry, UHMW is the most commonly used plastic for applications that require characteristics such as low friction, high wear and abrasion resistance, including conveyors, guides, static bearings, packaging, and many others.
Technical Details
How does UHMW come by its crazy powers, or its name, for that matter? The simple answer is; because the molecules that make up this particular thermoplastic are so long, when they get together, they stick like velcro and don’t like to let go.
More technically, many of UHMW’s attributes are directly related to the length of the molecules in its composition, and how those molecules interact with each other. Although it varies, the number of monomers (rings in the molecular chain) in each UHMW molecule is around 200,000 which, when compared to its close cousin HDPE’s average of 1,1000 monomers per molecule, gives you an idea of scale.
Although the van der waals forces which stick UHMW’s molecules together are not very strong, the sheer number of bonds means that on a macroscopic level they are incredibly tough to break, contributing to its abrasion and impact resistance.
Because each molecule’s chemical composition is free from phthalic acid esters, amides or hydroxylic groups, UHMW is impervious to moisture, most aggressive chemicals, and micro-organisms. Critically, UHMW’s inert chemical makeup means it can be used internally for things such as joint replacement wear surfaces.
UHMW can be molded into the final shape, extruded, sintered, or spun, with the last process delivering a lightweight high-strength oriented-strand product. UHMW strands can have a strength up to 350,000 psi and because they are so low density (0.97 g/cm3 vs. steel at 7.8 g/cm3) they are often used for high strength cable. The strength-to-weight ratio for UHMW is also about 140% that of aramid.
How is UHMW Processed?
Lasers and plastic don’t typically play well together, so to offer a wider variety of materials, we use CNC Routers to cut most plastics, including UHMW. Just about any information you might need to set up a part for CNC routing can be found on the Design Guidelines for CNC.
The cut tolerance on our CNC machines is still great at 0.005”, but remember that because the tooling is ⅛” diameter, that is the smallest hole size that can be specified in any of our UHMW thicknesses. Other details can be found on the UHMW Material page.
Because the part needs to be secure while being machined, each CNC cut part will have several fixture tabs.

Check out our Fixture Tab Guidelines for information on what to expect when your part comes off our equipment.
Designing with UHMW
At SendCutSend we currently offer UHMW in two sheet sizes; 0.375” and 0.500” which are great for guarding, wear parts, guides, gears, or just about any other flat part you can dream up.
Let’s look at a simple sliding part designed to be CNC routed from UHMW. Because it will move forward and back, the corners have been rounded, and two ¼” holes have been added for easy mounting.
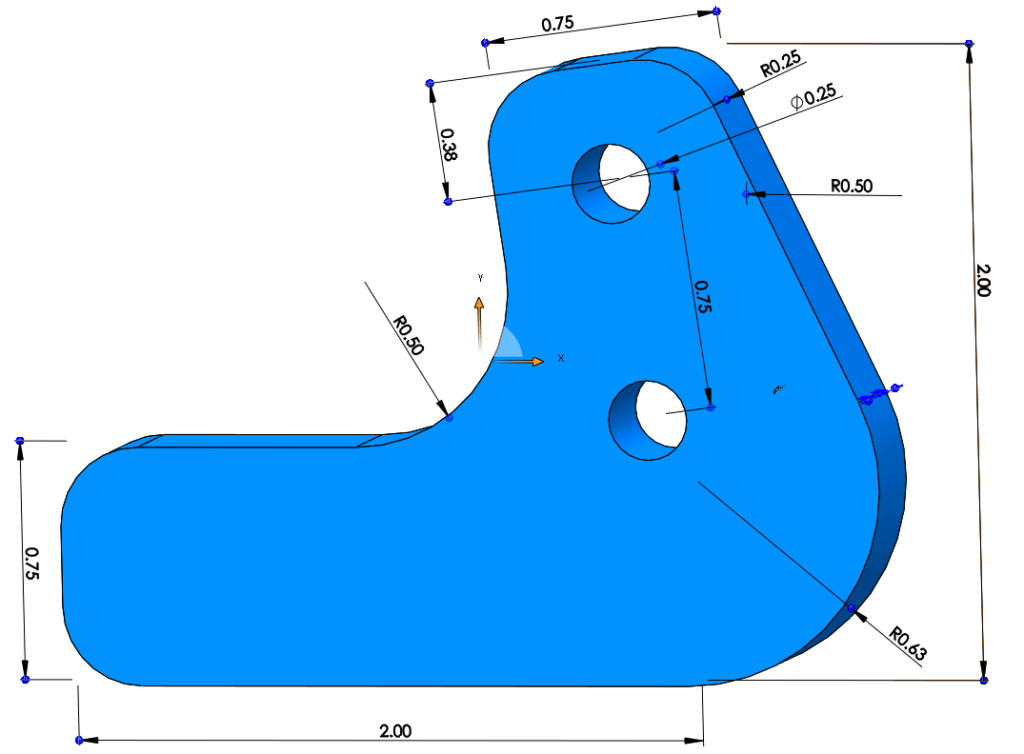
For critical dimensions such as minimum part size and hole-to-edge dimensions, reference the Material Page details.
Because it is self-lubricating and low friction, UHMW works well for low-speed, sliding contact parts. The design requirements for these parts have four slides supporting a total of 200 lbs and sliding at a maximum rate of 1 FPS for short bursts.
Note that because of localized heat buildup, rotational parts (think shaft bearings) should be made of a material with a higher working temperature.
For the back of the assembly, a similar design with slightly different angles and leading curvature is used. To get an idea of how the UHMW part will look, it has been rendered below.

Both of these sliding parts are shown at a ⅜” thickness, so after uploading the DXF files to the SendCutSend app we will select UHMW, pick our thickness, quantity, and add it to the cart. Done.
All that’s left is to wait a couple days for our parts to be cut and arrive at our door.
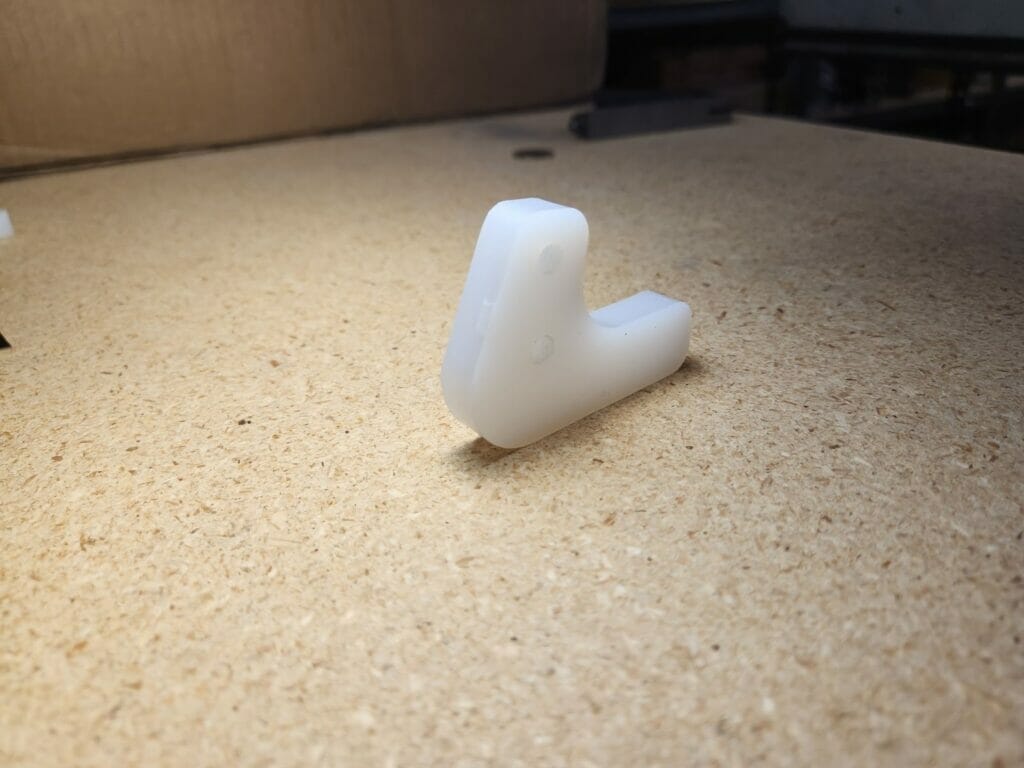

Caution: your SendCutSend parts may strongly resemble your CAD drawing.
UHMW Properties
Many of the unique properties of UHMW have already been highlighted, but several are worth mentioning here.
Inert
Because it doesn’t easily react with chemicals (other than some oxidizing acids), organic or inorganic, UHMW is odorless, tasteless and nontoxic, with the virgin material cleared for food service by the FDA.
Machinable
Although UHMW has around 12x the coefficient of thermal expansion of steel, because it is relatively soft, great results can be achieved by machining with standard tooling. Make sure to use sharp bits and blades which have not been used for metal (at least since being sharpened), keep the feed aggressive, and the holes clear of chips.
Low Energy, High Strength
Low weight and high strength, coupled with low-energy breakage due to its ability to elongate before failing, make UHMW an excellent alternative to steel cables and other cordage in numerous applications including winch cables, fishing line, and suspension lines for parachutes.
UHMW The Unassuming Hero
With some of the most outstanding properties of any plastic, and wear resistance better than most metal alloys, UHMW outperforms the many well-known materials in common applications: It is used extensively in personal ballistics protection, outperforming kevlar against high-caliber rounds, and is even found in some light vehicle armoring.
Although its maximum working temperature is lower than that of PTFE (Teflon), it can have 10x better wear resistance, making it the first choice for wiper/scraper blade applications.
For this reason, you can also find UHMW on almost any assembly line, or on parts with sliding contact surfaces. Particularly in food processing, UHMW is often the plastic of choice for containers, or conveyor belt components.
The best part? Although one might think these properties come at a high cost, UHMW is relatively inexpensive and readily available, and can be less than 1/10th the cost of PTFE.
With low minium pricing + free shipping, and multiple parts often costing just a few dollars each, our CNC machined UHMW is no exception. Upload your part today for instant pricing.





